David Amell/Android Authority
You may have heard much about it. Fifth generation networkRecently, 5G was announced as the next generation in mobile network technology. According to smartphone manufacturers and carriers, 5G could revolutionize how we stay connected on the move. However, 5G is not just hype. How fast will they actually work in the real world and how do they compare with existing 4G networks? Here’s everything you need.
Related: The best 5G plans in the US
The average 5G speed is currently around 100Mbps in the US, and that number is increasing with each passing month. T-Mobile is currently a fastest 5G carrier with average speeds of close to 200Mbps. If you aren’t seeing the same speeds, it is likely that you’re connected with a low-bandwidth (5G) network. Continue reading for more information.
What is the speed of 5G
Before we get into numbers it is worth understanding 5G and the reasons for its speed gains. 5G uses more spectrum than 4G, which allows for faster data transfer and greater capacity. This means that 5G connectivity will not be slow in dense urban areas. 4G LTElikely to struggle. This makes the former ideal to use for data-intensive apps, such as video broadcastCloud games.
However, a 5G signal does not always mean that you are getting the fastest connection. As you can see, 5G wireless spectrum is divided into 3 distinct frequency bands: low band, middle band, and high. The fastest frequencies, also known by mmWave (or MHzwave), offer super-fast speeds that rival previous cellular generations. You have probably seen or heard of 5G speeds exceeding 1Gbps. It is possible to achieve this speed on an mmWave Network.
Although mmWave 5G is not able to penetrate walls or other obstacles, mid-band 5G provides a good combination of speed and range.
but, mmWaveHe has some issues. Higher frequencies won’t be able to overcome obstacles, even when you consider the high infrastructure costs of building towers on a large scale. Your phone will have trouble maintaining a mmWave signal indoors in the real-world. Even if signal is not lost completely, your phone will experience slower data transfers as well as higher latency.
To combat this problem, carriers often deploy mmWave technology that penetrates low and medium-band networks. The low band uses frequencies similar in frequency to 4G. This means that you can get reliable coverage regardless of whether you are indoors or out. As we’ll see in the next section, the midrange provides a healthy balance between range and performance.
Continue reading: Why sub-6GHz 5G is more important than mmWave
It is important to note that not all devices can support mmWave5G technology. The most popular flagship smartphones are the ones that come in the range of The GoogleApple and Samsung include the hardware in the US. If you are not in the US, or have an unlocked device, mmWave 5G connectivity may not be available to you.
Check out our list. The best 5G phones you can buy right now
Comparison of 5G and 4G LTE speeds in numbers: Which one is faster?
We now know how 5G spectrum works so it shouldn’t surprise that there might be huge fluctuations in download speeds between networks.
5G speeds exceeding 100Mbps have become more common, however, performance is highly dependent upon frequency band and signal strength.
mmWave network speeds can be up to 1Gbps in the real-world, while speeds on the lower end are possible with mmWave. Your smartphone’s theoretical limit is 10Gbps. SoCAnd the modem will not be able to keep pace. Additionally, obstructions like tree cover can slow down download speeds and signal quality.
The low-band 5G spectrum is on the other end. It doesn’t offer a lot of bandwidth, but can easily cover several hundred miles at once. This is the slower type, so you can’t expect faster performance from 4G.
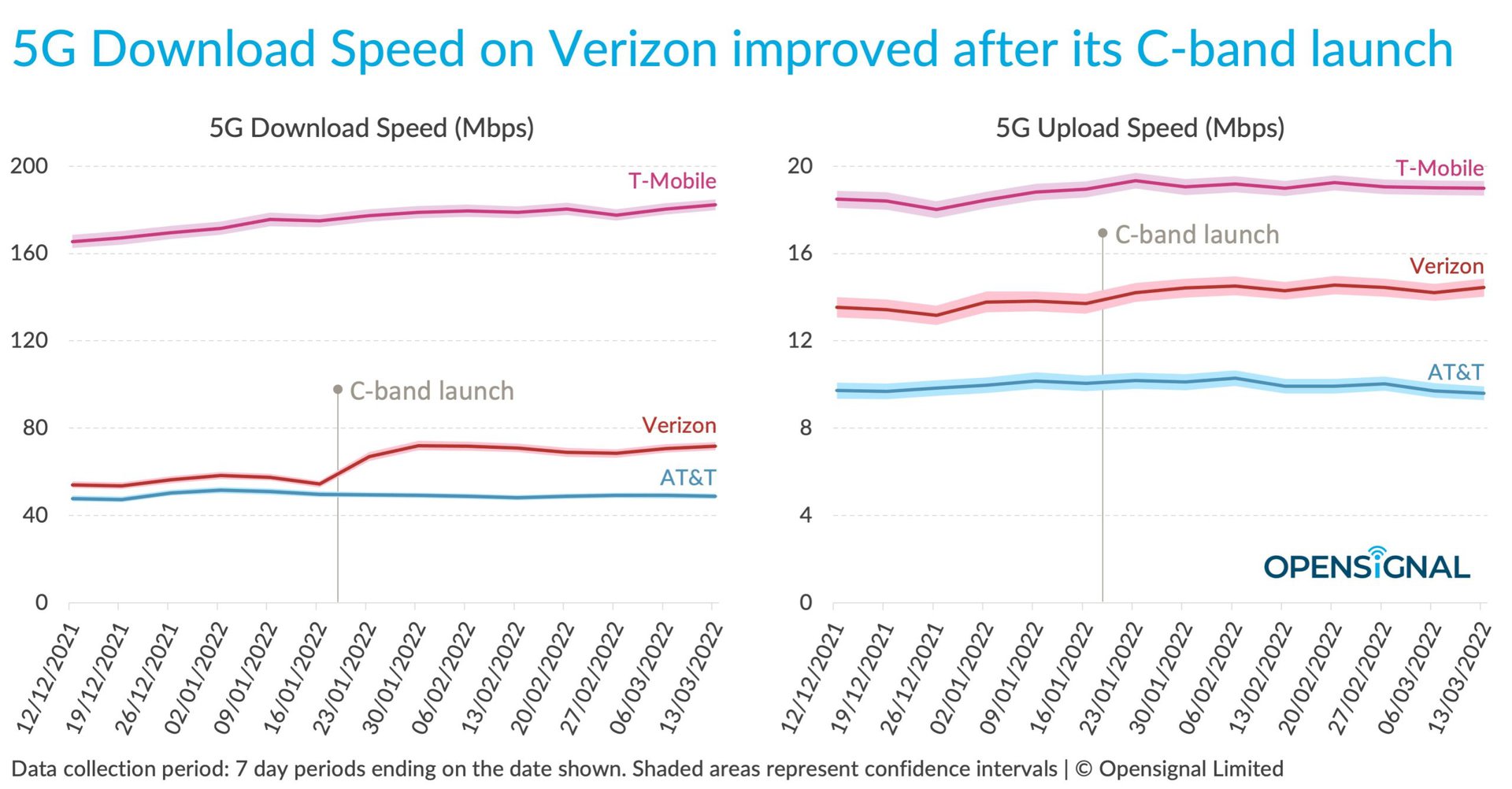
The mid-band 5G network is the final option. You may also be referred to it as C BandIn the United States. It can offer speeds between 100 and 900 Mbps, which are quite fast for most uses cases. Mid-band 5G networks are considered the best balance of speed and coverage by most carriers around the globe. While you don’t lose as many coverage as with mmWave networks, you still get speed on lower frequencies. The US is beginning to see C-band deployments grow in momentum. We can expect to see significant speed increases in the near future.
According to the tests, he passed. OpenSignalVerizon’s CBand boosted 5G speeds by 25%. The graph shows that Verizon’s average 5G data download speeds increased significantly after it brought its CB infrastructure online in the early 2022. T-Mobile and Verizon both consistently deliver fast download speeds, even if you look at their mid-band 5G results. More than 200 Mbps
Is carrier selection important? Which US carrier has the fastest speeds for 5G?

Chris Carlon/Android Authority
In the United States T-MobileHe currently leads both VerizonThen there’s the at & vIn terms 5G speeds. Ookla will be launching 5G speeds in the third quarter 2022. have foundT-Mobile was nearly twice as fast downloading as Verizon in the average download speed. These results were compatible with OpenSignal the findingsT-Mobile’s average speeds were estimated at just over 170Mbps by a similar study. T-Mobile currently trails Verizon and At&t by about 100Mbps.
Average 5G speeds are around 100Mbps in the US. However, you can expect to see better results in the near future.
However, not everyone requires the fastest network. Verizon’s average download speed, 100 Mbps, will likely satisfy most customers’ needs. Your location could produce different results from the reports above depending on factors like the number of users and the proximity to the nearest mobile tower. You can find the coverage maps of the carriers that offer the best 5G service to your needs by looking at them. thisT-Mobile
Remember that carriers sometimes use their branding to identify mmWave frequencies and midband frequencies. Verizon, for instance, uses 5G Nationwide (or 5G Ultra Broadband) to distinguish the two. T-Mobile customers might notice a 5G UC sticker on their smartphones when they are connected to the fastest 5G networks.
Continue reading: What does 5G UC mean?
How to measure 5G speeds using your phone
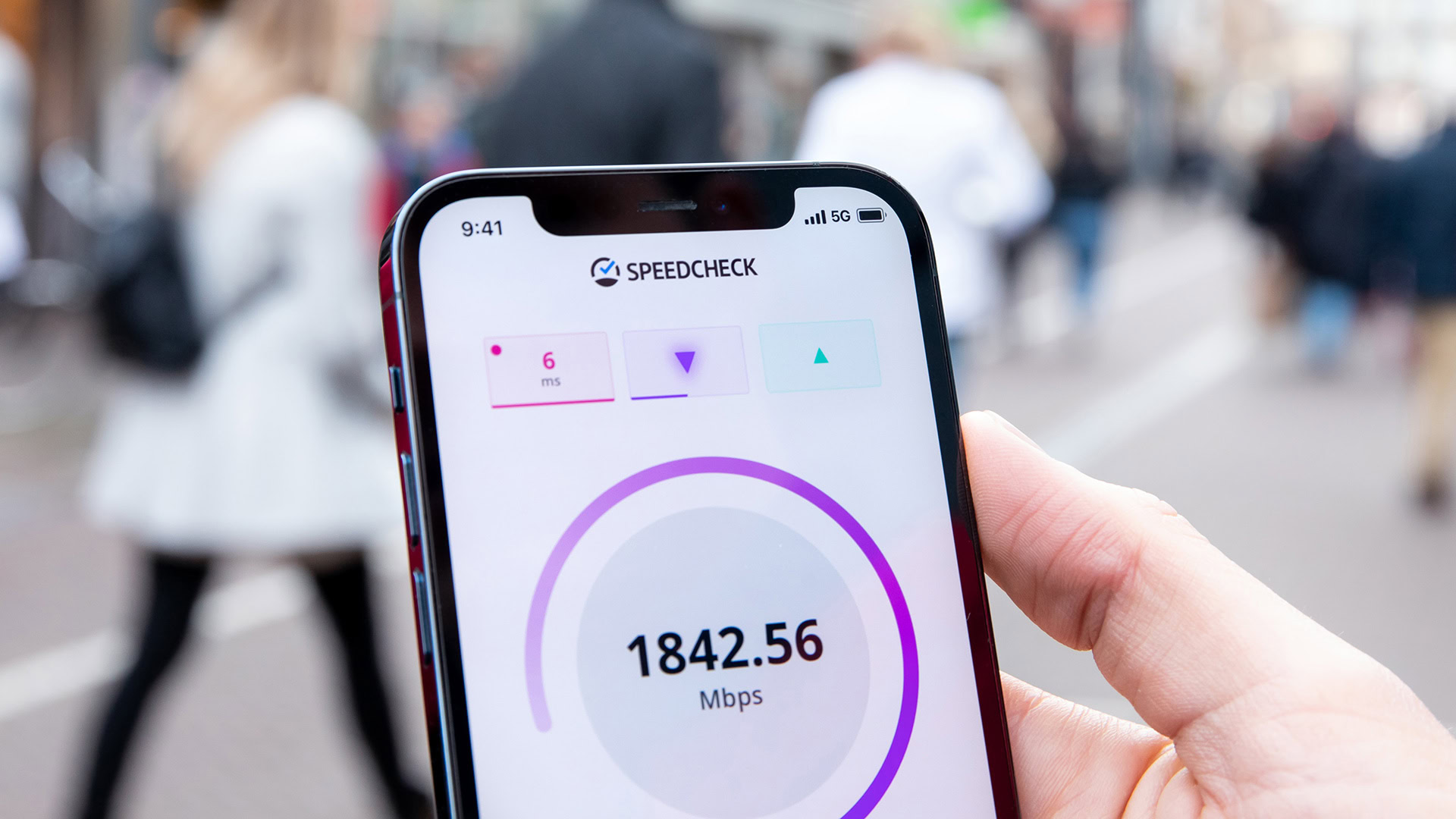

A speed test can help you determine how fast your 5G connection is working. Simply open fast.comOr speedtest.netUse a web browser to access the test from your smartphone. You can also download the app from Android Play StoreTo do the same, you can use the iOS App Store. Make sure you are not connected to Wi-Fi and your phone is receiving a 5G signal.
In general, speeds exceeding 100Mbps will require an upgrade to most 4G LTE networks. If your phone can reach gigabit speeds it is likely that you are connected to an mmWave network or Band C network.
Questions and answers
5G networks work at low, medium, and high frequencies. Low band frequencies (less that 1 GHz) have shorter wavelengths, so they can penetrate walls and other obstructions better than higher frequencies. Speeds will not be faster than 4G due to lower frequencies’ bandwidth and capacity.
It is unfair to compare 5G with WIFIBecause speed is highly dependent on the infrastructure. You can pay more per month for faster broadband (WiFi) speeds. However, you cannot control the quality of the 5G network when you travel from one place to the next.
Cellular networks use lower frequencies in order to increase range. You may notice a greater signal strength on older networks due to 5G using higher frequencies to reach greater capacity and faster speeds.
The claims of superfast 5G speeds that you have heard about don’t always hold in internal testing. This is because high-bandwidth frequencies can be easily blocked by walls and other obstructions. Even if your 5G towers are in good condition, monthly data caps will still apply to residential Wi-Fi connections. These caps are often much higher than the ones you have. So Can 5G replace Wi-Fi?Is it for good? Perhaps in the future, but not soon.
Source link
[Denial of responsibility! reporterbyte.com is an automatic aggregator of the all world’s media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, all materials to their authors. If you are the owner of the content and do not want us to publish your materials, please contact us by email – reporterbyte.com The content will be deleted within 24 hours.]